Chapter 10: Emerging Technologies and the Future of Business
Learning Objectives
Welcome to the final chapter! Technology is always moving forward, creating new opportunities and challenges. After studying this chapter, you will be able to:
- Describe Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) and their business applications.
- Explain the growing role of cloud computing in modern business.
- Identify other emerging technologies like big data and blockchain.
- Understand the importance of continuous learning and adaptability in a technology-driven world.
- Recognise the need for critical and responsible thinking when using future technologies.
Introduction
Throughout this book, we have explored the foundational concepts of computing, from the hardware inside your laptop to the vast network of the internet. But technology does not stand still. The tools we use today are vastly more powerful than those from just a few years ago, and the technology of tomorrow promises even more profound changes.
For anyone preparing to enter the business world, understanding the next wave of technological innovation is not just an interesting academic exercise; it is an essential requirement for success. The forces of automation, data analysis, and hyper-connectivity are fundamentally reshaping industries, creating new business models, and demanding new skills from the workforce.
In this final chapter, we will look forward, exploring some of the exciting emerging technologies that are already beginning to transform how businesses operate in Malaysia and around the globe. We will demystify complex topics like Artificial Intelligence and the Internet of Things, explore the foundational role of cloud computing, and touch upon other game-changing concepts like big data and blockchain.
This is not just a tour of futuristic gadgets. This is a guide to understanding the forces that will shape your future career. It will help you prepare for a world where being adaptable, curious, and committed to lifelong learning is the most valuable skill you can possess.

Artificial Intelligence (AI): The New Engine of Business
We introduced the concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI) earlier in the book. At its core, AI is a broad field of computer science focused on creating smart machines and software capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. This is not about creating conscious robots like in the movies. Instead, it is about developing systems that can perform specific intelligent functions, such as learning from data, solving complex problems, understanding human language, and recognizing patterns.
AI is no longer a futuristic concept confined to research labs; it has become a powerful and practical business tool that is being integrated into almost every industry.
The Business of AI: From Chatbots to Fraud Detection
Companies are leveraging AI to become more efficient, make smarter decisions, and provide better experiences for their customers.
A very common application that you have likely interacted with is the customer service chatbot. When you visit the website of a Malaysian telecommunications company like Maxis or a bank like CIMB, a small chat window often pops up, asking if you need help. This is usually an AI-powered chatbot. It uses a branch of AI called Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand your typed questions and provide instant answers to common queries, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. This frees up human customer service agents to handle more complex problems, improving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Another powerful application is in e-commerce. When you browse a site like Lazada or Shopee, the platform is constantly analyzing your behaviour: what you search for, what you click on, what you buy. It uses a type of AI called machine learning to build a recommendation engine. This is the system that shows you a personalized list of “Products you might like.” By predicting what you are likely to be interested in, these companies can significantly increase their sales.
In the financial world, AI is a crucial tool for security. Banks use sophisticated AI algorithms to analyze thousands of transactions per second, looking for patterns that might indicate fraud. If a transaction suddenly occurs on your Maybank credit card in a different country while you are in Malaysia, an AI system can instantly flag it as suspicious and block the transaction, protecting you from theft.
The Malaysian government recognizes the transformative potential of AI. Through agencies like the Malaysia Digital Economy Corporation (MDEC), it is actively promoting AI adoption across key sectors to boost the nation’s competitiveness. The goal is to use AI to improve everything from the efficiency of manufacturing plants in Penang to the accuracy of medical diagnoses in hospitals in Kuala Lumpur..
The Internet of Things (IoT): A World of Connected Devices
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the vast and growing network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that connect them to the internet, allowing them to collect and share data. These are not just your computer and smartphone. They are everyday objects that have been given a digital “voice.”
Think of it this way: the original internet was a network connecting computers. The mobile internet connected our personal devices. The IoT is the next evolution, where the internet connects almost everything.
The Impact of IoT on Business: Creating “Smart” Industries
The true power of IoT for business is its ability to gather immense amounts of real-time data from the physical world. This data allows companies to monitor their operations, automate processes, and make data-driven decisions with a level of precision that was previously impossible.
A great local example is in the Malaysian logistics industry. A company that transports frozen goods from a port in Klang to supermarkets across the country can use IoT to create a “smart” supply chain. Each of their refrigerated trucks can be equipped with IoT sensors that constantly monitor and transmit data about the truck’s exact GPS location, the temperature inside the cargo container, and even the fuel level of the truck. A manager in the head office can view all of this information in real-time on a single dashboard. If the temperature in one of the trucks starts to rise, the system can send an automatic alert to the driver and the manager, allowing them to fix the problem before the valuable cargo spoils.
In agriculture, a farmer managing a large palm oil plantation in Sabah can use IoT devices to create a “smart farm.” IoT sensors can be placed in the soil to monitor moisture levels and nutrient content. Drones equipped with cameras can fly over the plantation to check for signs of disease. This data is all sent to a central system, which can then automatically control the irrigation system to deliver water only when and where it is needed, conserving a precious resource and improving the health and yield of the crops.
This ability to connect the physical and digital worlds is creating “smart factories,” “smart cities,” and “smart agriculture,” all of which are more efficient, productive, and sustainable.

Cloud Computing Revisited: The Foundation of Modern Business
We have mentioned cloud computing before, but it is impossible to overstate its importance to the future of business. Cloud computing is the delivery of a wide range of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet (“the cloud”).
Instead of a company buying, owning, and maintaining its own physical computing infrastructure (which is very expensive), it can rent access to these services from a cloud provider. The three largest global cloud providers are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure.
The Growing Role of the Cloud in the Digital Economy
The cloud has become the essential backbone of the modern digital economy. For businesses, especially Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), which are the heart of the Malaysian economy, cloud computing is a game-changer.
Imagine a group of recent university graduates in Labuan who want to start a new e-commerce business. In the past, they would have needed a huge amount of money to buy their own powerful servers to run their website, hire an IT team to manage them, and rent a secure, air-conditioned room to store them in. This massive upfront cost would have been a major barrier to starting their business.
With cloud computing, they don’t need any of that. They can simply rent a “virtual server” from a provider like AWS for a small monthly fee. They get access to world-class, powerful computing infrastructure without the large capital investment. This dramatically lowers the barrier to entry for new startups.
The cloud also provides incredible flexibility and scalability. During a normal month, the startup might only need a small amount of computing power. But during a big sales event like Hari Raya, they expect a huge surge in traffic to their website. With the cloud, they can instantly “scale up” their services, renting more computing power for just the few days they need it, and then “scale down” again afterwards. They only pay for what they use, just like electricity.
Furthermore, the cloud enables modern, flexible work. By using cloud-based software like Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace, employees can access their files and collaborate on documents from anywhere in the world, as long as they have an internet connection. This is what makes remote work possible.
Malaysia is rapidly becoming a major hub for data centers in Southeast Asia, with global giants like Microsoft and Google investing billions of Ringgit to build massive facilities here. This shows just how central cloud computing is to the region’s current and future economic growth.

Check Your Understanding: Q1
Check Your Understanding: Q2
Check Your Understanding: Q3
Other Emerging Technologies Shaping the Future
Several other powerful technologies are also converging to shape the future of business.
- Big Data: This term refers to the extremely large and complex sets of data that are generated every second by all of our online activity, the billions of IoT devices, and countless business transactions. The sheer volume, velocity, and variety of this data are so great that it cannot be managed or analyzed using traditional data-processing tools. The key is not just collecting the data, but using powerful computers and AI algorithms to perform data analytics. This means sifting through the noise to find hidden patterns, market trends, and valuable insights that can help businesses make smarter, evidence-based decisions.
- Blockchain: To understand the revolutionary nature of blockchain, it is helpful to first consider a traditional system for recording information, such as a bank’s ledger.
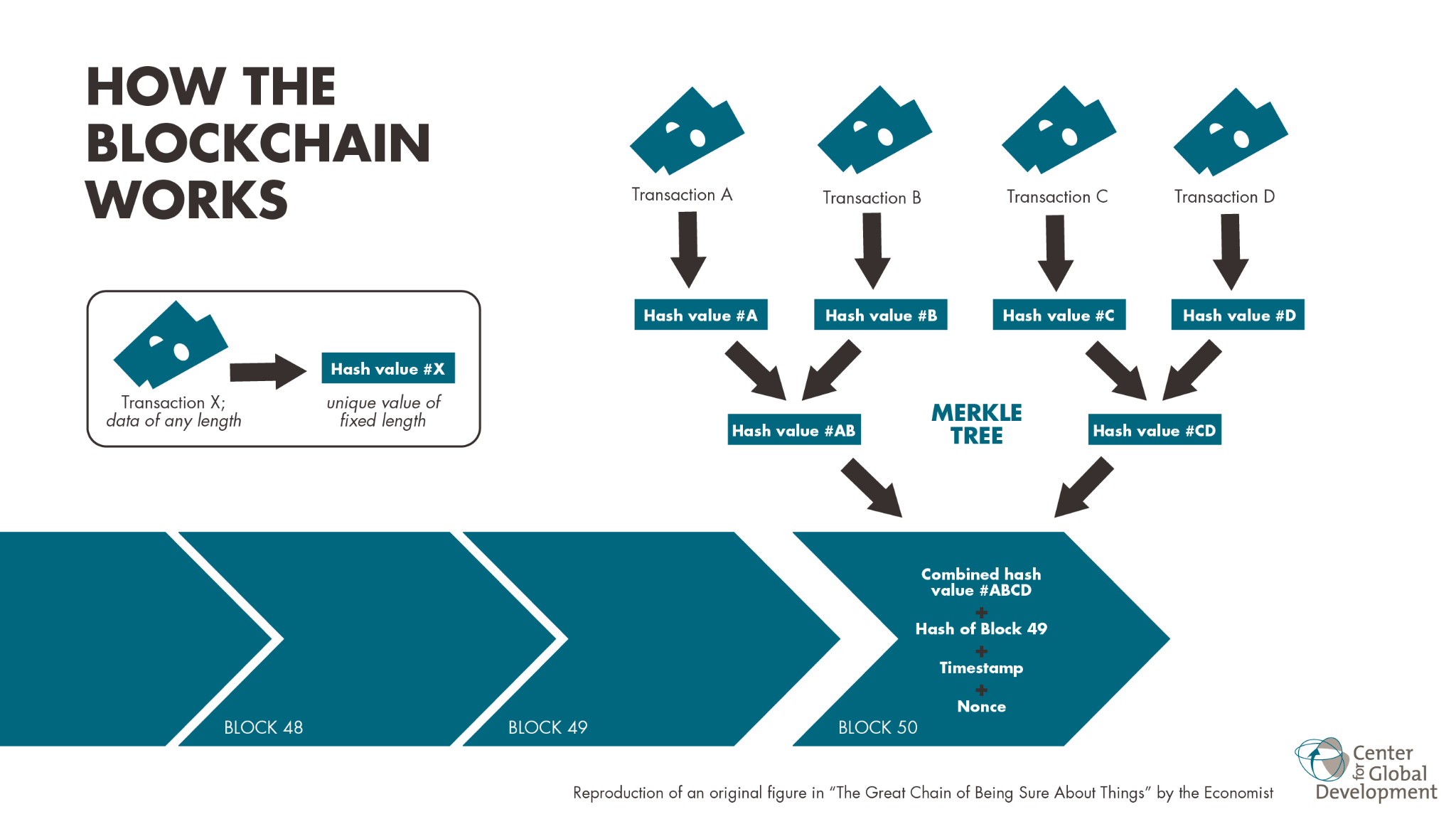
- This familiar system is centralized, meaning a single entity, the bank, owns, controls, and is solely responsible for the accuracy of all transaction records. We trust the bank to maintain this ledger honestly and securely. Blockchain technology reimagines this entire concept by creating a system that does not require trust in a central authority. At its core, a blockchain is a secure, decentralized, and distributed digital ledger. Instead of being held in one private location, this unique ledger is shared identically across a vast network of computers, with each participant holding a complete copy.
- The true innovation lies in how new information is added. When a new transaction or record is created, it is bundled together with other recent transactions into a new “block.” This block is then cryptographically sealed, creating a unique digital fingerprint. It is then permanently linked to the block that came before it, forming an unbreakable and chronological “chain.” A full and updated copy of this entire growing chain is then distributed to every computer participating in the network.
- This distribution is what makes the blockchain so incredibly secure and transparent. For a bad actor to secretly alter a past transaction, they would face an impossible task. They could not simply change the record on one computer; they would need to simultaneously find and alter the majority of the identical copies of the ledger spread across the global network, all while continuously recalculating the cryptographic links of every subsequent block in the chain. The sheer scale of this computational challenge makes the system effectively tamper proof. This creates a shared history of events that everyone on the network can see and agree upon without needing to trust a middleman.
- While blockchain technology is most famous for powering cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, its potential for business extends far beyond digital money. Companies are now exploring its ability to create unprecedented levels of transparency and security in fields like supply chain management. Consider a company in Malaysia that exports premium Musang King durians to a discerning market in China. By using a blockchain, the company can create a verifiable and unchangeable story for its product. The initial certification of the farm in Pahang could be the first block. The date of harvest and batch number could form the next. Each step, from clearing customs at the port to the temperature logs inside the shipping container, would be added as a new, permanent block in the chain. A customer in a Shanghai supermarket, curious about the product’s origin, could then simply scan a QR code on the fruit to see its entire secure journey, providing absolute proof of its authenticity and quality.
- Automation: This is the use of technology to perform tasks that were previously done by humans. This ranges from physical robotics (like the robotic arms that assemble cars in a Proton factory) to Robotic Process Automation (RPA), which is software that can be programmed to automate repetitive digital tasks, like processing invoices or transferring data between different software systems. The goal of automation is to help businesses increase efficiency, reduce errors, and free up human employees to focus on more creative and strategic work.
- Cybersecurity Trends: As businesses become more digital and connect more devices to the internet, their “attack surface” grows, making them more vulnerable to cyber threats. Consequently, the need for advanced cybersecurity becomes more critical than ever. New and more sophisticated threats appear all the time, so cybersecurity is a field that is constantly evolving. Future trends include using AI to predict and automatically respond to cyberattacks and developing new security models for the vast and complex world of IoT devices.
Staying Updated: The Importance of Continuous Learning
With the pace of technological change accelerating so rapidly, the single most important skill you can possess for a successful career is the ability and willingness to learn and adapt.
The specific software you master in university today might be outdated in five years. The programming language that is in high demand now might be replaced by a new one in the next decade. However, if you have a strong foundation in the fundamental concepts of computing (like the ones covered in this book) and, more importantly, a mindset of continuous learning, you will always be able to adapt to what comes next.
Continuous learning means actively seeking out new knowledge and skills throughout your career. This could involve taking online courses, attending industry workshops and seminars, reading books and articles about new technologies, and earning professional certifications.
In Malaysia, there is a widely recognized “digital skills gap.” This means that there are not enough workers who possess the advanced technology skills that modern companies desperately need. This situation presents a huge opportunity for students and young professionals who are committed to keeping their skills up to date. By becoming a lifelong learner, you are not just keeping yourself relevant; you are making yourself highly valuable in the job market.
Critical Thinking and Responsible Technology Use
Finally, as we stand on the cusp of this new technological era, we must do more than just learn how to use these powerful new tools. We must also think critically and act responsibly.
The rise of AI, automation, and big data collection raises profound and important ethical questions that society is still grappling with.
- Privacy: How much of our personal data are we willing to give up in exchange for convenient services?
- Fairness and Bias: AI systems learn from the data they are trained on. If that data reflects existing societal biases, the AI can learn and even amplify those biases, leading to unfair outcomes in areas like hiring or loan applications.
- The Future of Jobs: As automation technology becomes more capable, what will be the impact on the human workforce? Which jobs will be replaced, and what new jobs will be created?
As a future business professional, it will be your responsibility to use these tools not just to create profit, but to do so in a way that is ethical, transparent, and benefits society. The future of technology is not just about what technology can do; it is about what we, as responsible humans, choose to do with it.
Check Your Understanding: Q4
Check Your Understanding: Q5
Check Your Understanding: Q6
Chapter Summary
In this final chapter, we have taken a look into the near future of business and technology. We explored powerful and transformative emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), the ever-important cloud computing, big data, and blockchain. We learned that these are not just buzzwords; they are powerful tools that are already being used to create smarter, more efficient, and more data-driven ways of doing business in Malaysia and across the globe.
Most importantly, we understood that in a world of constant and accelerating change, technical skills alone are not enough. The commitment to continuous learning and the practice of responsible, critical, and ethical technology use are the true keys to building a successful and meaningful career in the exciting and challenging decades to come.
Review Questions
- Describe one way a business in Malaysia could use AI and one way it could use the Internet of Things (IoT).
- What is cloud computing? Explain why it is particularly useful for a small or new business (SME) compared to the traditional way of owning IT infrastructure.
- Using the analogy of a shared digital notebook, explain in your own words what a blockchain is and why it is so difficult to tamper with.
- Why is continuous learning so important for a career in the modern business world? What is the “digital skills gap”?
- What is one ethical question that a business should consider before implementing a new technology like AI in its hiring process?
References
e27. (2024, November 14). Bridging the digital divide: Addressing Malaysia’s skills gap. https://e27.co/bridging-the-digital-divide-addressing-malaysias-skills-gap-20241114/
Laudon, K. C., & Laudon, J. P. (2020). Management information systems: Managing the digital firm (16th ed.). Pearson.
New Straits Times. (2025, July 3). Malaysia continues to lead regionally for digital infrastructure – BMI. https://www.nst.com.my/business/corporate/2025/07/1239810/malaysia-continues-lead-regionally-digital-infrastructure-%E2%80%93-bmi
Schwab, K. (2017). The fourth industrial revolution. Crown Business.
The Malaysian Reserve. (2025, February 13). 5G Advanced game changer for Malaysian industries. https://themalaysianreserve.com/2025/02/13/5g-advanced-game-changer-for-malaysian-industries/
A broad field of computer science focused on creating machines and software that can perform tasks requiring human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, and understanding language.
A vast network of physical devices (not just computers) that are embedded with sensors and connected to the internet, allowing them to collect and share data.
The delivery of on-demand computing services—including servers, storage, databases, and software—over the internet from a cloud provider.
Extremely large and complex data sets that can be analyzed computationally to reveal patterns, trends, and associations, especially relating to human behaviour and interactions.
The process of examining large data sets to find trends, draw conclusions, and make informed decisions.
A secure, decentralized, and distributed digital ledger technology that records transactions in a way that is highly resistant to modification.
A digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security, with Bitcoin being the most well-known example.
The use of technology to perform tasks with reduced human assistance.
The ongoing, voluntary, and self-motivated pursuit of knowledge for either personal or professional reasons.
The difference between the digital skills that employers need and the skills that the current workforce possesses.

